Parathyroid Disease
 Most people do not know that they have one parathyroid, let alone four of them, but the parathyroid glands serve a very important purpose – to regulate calcium levels in the body.
Most people do not know that they have one parathyroid, let alone four of them, but the parathyroid glands serve a very important purpose – to regulate calcium levels in the body.
Calcium
It is a well known fact that calcium makes strong bones and teeth. Less well known is the fact that our muscular and nervous systems also need calcium in order to function properly. The four parathyroid glands, usually located in the neck, just behind the thyroid gland, regulate blood calcium levels to ensure proper distribution of this mineral.
When blood calcium levels fall too low the parathyroid glands produce a hormone called parathyroid hormone or PTH. PTH signals the body to release calcium from the bones and into the bloodstream where it can be carried to the organs that need it. When blood calcium levels reach certain levels the Parathyroid glands will slow or even shut down PTH production.
Primary Hyperparathyroidism
Parathyroid disease, also called primary hyperparathyroidism, results when one or more of the parathyroid glands grows abnormally and becomes a non-cancerous tumor. When this happens the over grown gland(s) produces an excess of PTH, robbing the bones of calcium and overloading other systems. Over time, high blood calcium can impact the liver, kidneys, arteries, heart, stomach, and nervous system.
Symptoms of Hyperparathyroidism
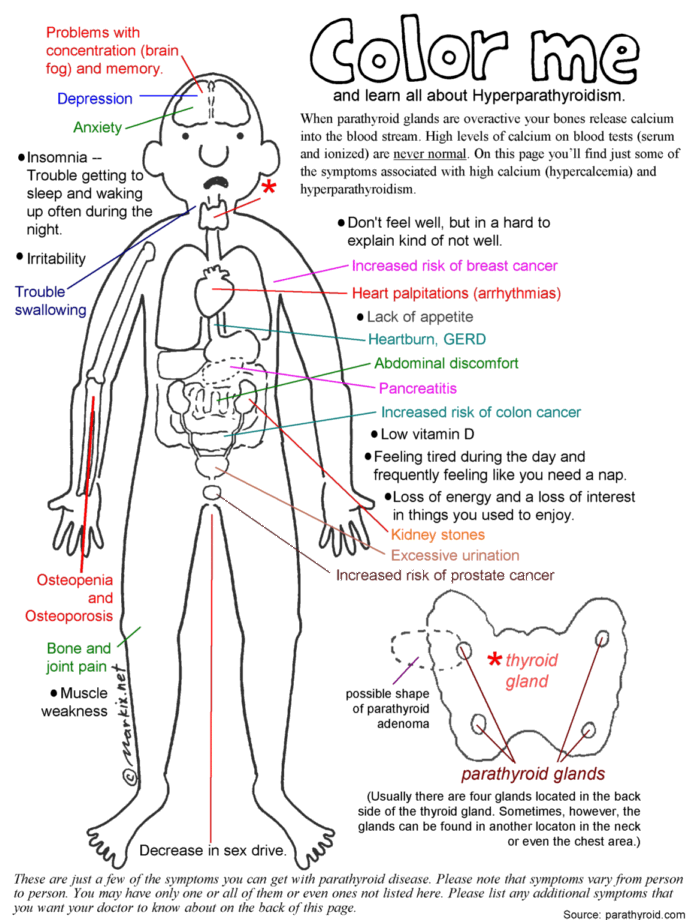
Since calcium is used by the nervous system hyperparathyroidism will usually impact the way a person feels. Many patients experience an inability to concentrate, low energy levels, depression, irritability, trouble sleeping, memory troubles, loss of interest in activities, and fatigue. Physical symptoms can include kidney stones, high blood pressure, recurrent headaches, heart palpitations, acid reflux (heartburn) and pain in the bones. All patients with primary hyperparathyroidism will eventually develop osteoporosis (thinning of the bones).
Diagnosis of Hyperparathyroidism
Simple blood tests can detect hyperparathyroidism. Your doctor will check your serum calcium levels; if the serum calcium is elevated (above 10.4) your doctor will then check your PTH levels. If PTH levels are also high then the patient is diagnosed with hyperparathyroidism. However, it is possible to have high calcium levels, but not high PTH levels. High calcium levels are always a concern and should not be ignored just because they are “slightly elevated” or do not coincide with elevated PTH levels.
Another test used to diagnose parathyroid disease is a sestamibi scan. When undergoing a sestamibi scan the patient will be injected with a mild radioactive agent which is absorbed by the overactive parathyroid gland. The tumor can then be identified via X-ray. To get an accurate reading this test is best performed by an experienced technician.
Treatment of Hyperparathyroidism
Surgery is the only effective treatment for hyperparathyroidism. If the overactive parathyroid gland is not removed it will continue to produce too much PTH, causing damage to the bones and other organs. There are two variations of parathyroidectomy surgery. The first was pioneered in 1925 and involves dissecting the patient’s neck in order to examine each of the four parathyroid glands. Once the bad gland (or glands) has been identified it is removed and the patient is stitched back up leaving a large scar behind. Fortunately, modern technology has made a minimally-invasive parathyroidectomy possible. This mini-surgery involves the use of radioactive isotopes pre- and intraoperatively in order to locate the parathyroid tumor and remove it. This surgery uses lighter anesthesia, a smaller incision, and dramatically reduced recovery time.
Minimally invasive parathyroidectomy, when preformed by an experienced surgeon, has a 99% cure rate. Even patients who had not noticed their symptoms prior to surgery have commented that they feel better afterward. Many patients will also experience dramatic resolution or related issues such as hypertension (high blood pressure), acid reflux, and depression.
If you or someone you know has had a blood test that shows high serum calcium levels it is recommended that you see a specialist in the area of Parathyroid disease. Since this is a rare condition many doctors, and even endocrinologists, do not fully understand it. One excellent resource is the website www.parathyroid.com run by the Norman Parathyroid Clinic in Tampa Bay, Florida.


Comments are closed.